Algorithm 算法
一般算法
查找句子频率出现最高的单词
- 题目
- 答案
const article = "This is a pen, a pencil.";
const findMostWord = (article) => {
// ...
}
findMostWord(article) // ['a', 2]
const article = "This is a pen, a pencil.";
// 思路
// 用 split() 来将句子中的单词拆分成数组
// 然后用 for 循环遍历数组,使用一个对象来记录每个单词出现的次数
// 最后遍历对象,找出频率最高的单词
const findMostWord = (article) => {
// 将句子拆分成单词
const words = article.split(" ");
// 创建一个对象来记录每个单词出现的次数
const wordCount = {};
for (let i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
const word = words[i];
if (wordCount[word]) {
wordCount[word]++;
} else {
wordCount[word] = 1;
}
}
let mostWord;
let maxCount = 0;
for (let word in wordCount) {
if (wordCount[word] > maxCount) {
maxCount = wordCount[word];
mostWord = word;
}
}
return [mostWord, maxCount]
}
findMostWord(article)
小孩报数(约瑟夫环)问题
- 题目
- 答案
// 有 30 个小孩,编号从 1 到 30,围成一圈依次报数 1、2、3
// 数到 3 的小孩儿退出这个圈,然后下一个小孩重新报数 1、2、3
// 问最后剩下的那个小孩儿的编号是多少?
// 有 30 个小孩,编号从 1 到 30,围成一圈依次报数 1、2、3
// 数到 3 的小孩儿退出这个圈,然后下一个小孩重新报数 1、2、3
// 问最后剩下的那个小孩儿的编号是多少?
let children = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
children[i] = i + 1;
}
let exitCount = 0; // 离开人数
let count = 0; // 记录报数
let index = 0; // 当前下标
while (exitCount < 30 - 1) {
// 如果当前小孩未退出
if (children[index] !== 0) {
count++;
}
if (count === 3) {
// 将退出的小孩在数组中编号标记为 0
children[index] = 0;
count = 0;
exitCount++;
}
index++;
if (index === 30) {
index = 0
};
}
const result = children.filter((item) => item !== 0)
console.log(result[0])
【LC】20. 有效的括号
https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/
- 题目
- 答案
输入:s = "()"
输出:true
输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true
输入:s = "(]"
输出:false
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValid = function (s) {
// ...
};
输入:s = "()"
输出:true
输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true
输入:s = "(]"
输出:false
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValid = function (s) {
if (s.length % 2 !== 0) {
return false
}
const arr = s.split('')
const stack = []
for (let i = 0, len = arr.length; i < len; i++) {
if (['(', '[', '{'].includes(arr[i])) {
stack.push(arr[i])
} else {
const top = stack[stack.length - 1]
if (
top === '(' && arr[i] === ')' ||
top === '[' && arr[i] === ']' ||
top === '{' && arr[i] === '}'
) {
stack.pop()
} else {
return false
}
}
}
if (stack.length > 0) {
return false
}
return true
};
【LC】76. 最小覆盖子串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-window-substring/
- 题目
- 答案
输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
输出:"BANC"
解释:最小覆盖子串 "BANC" 包含来自字符串 t 的 'A'、'B' 和 'C'。
/**
* @param {string} s
* @param {string} t
* @return {string}
*/
var minWindow = function (s, t) {
const arr = s.split('')
};
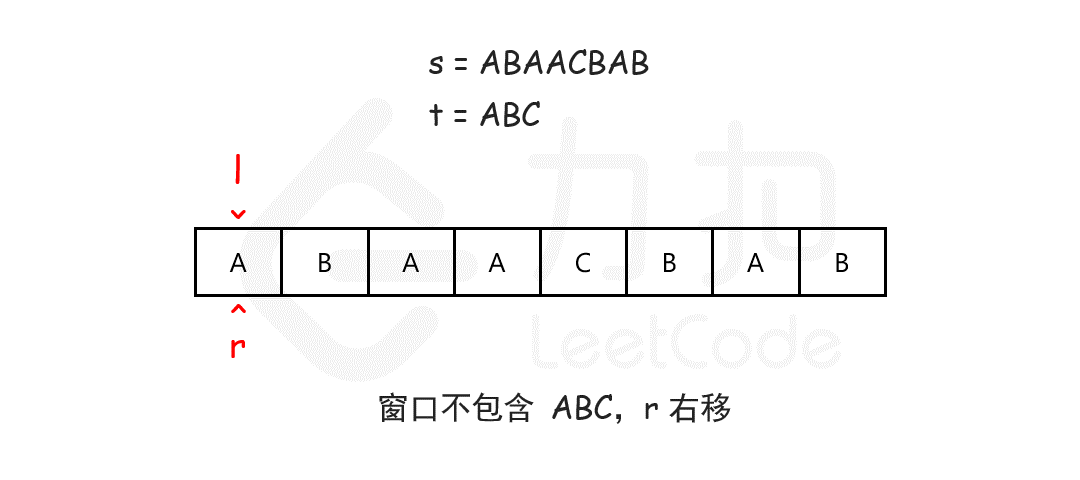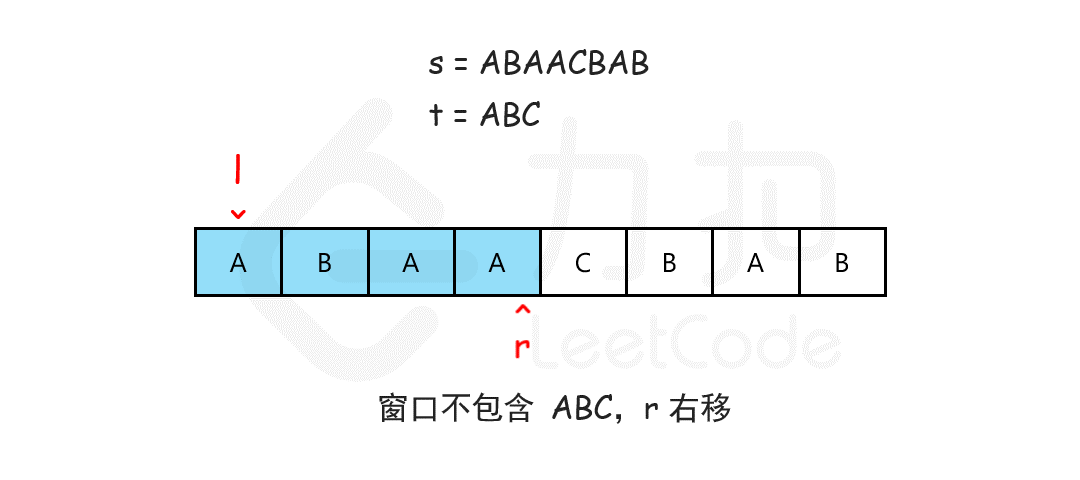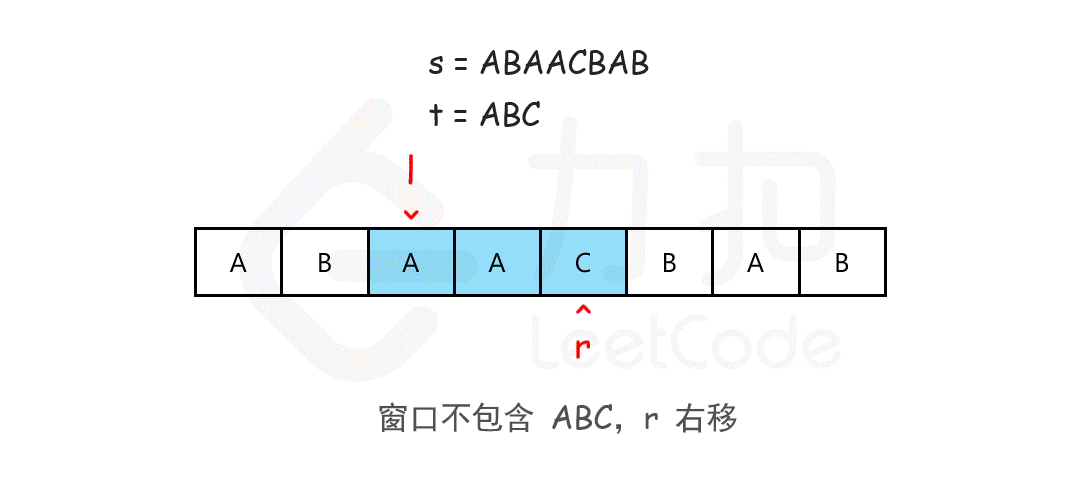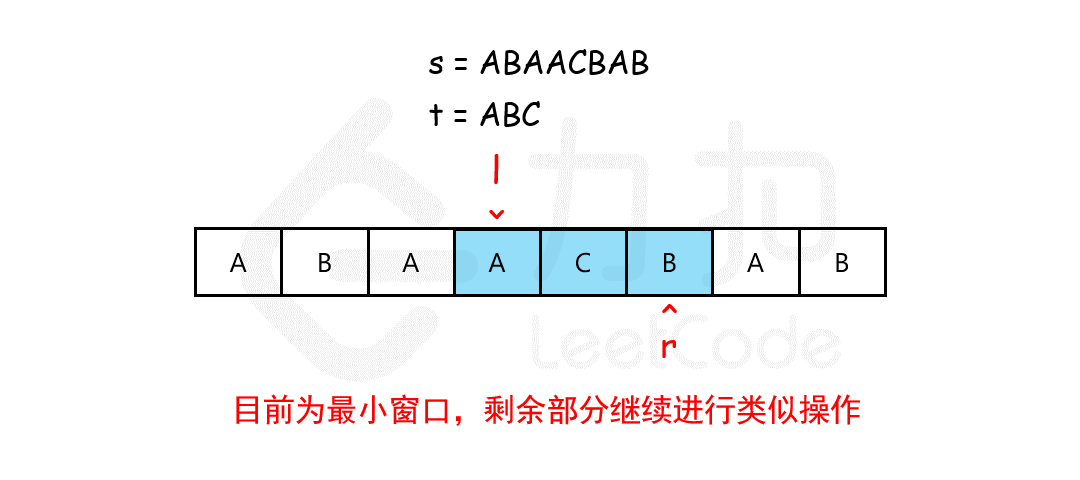
输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
输出:"BANC"
解释:最小覆盖子串 "BANC" 包含来自字符串 t 的 'A'、'B' 和 'C'。
/**
* @param {string} s
* @param {string} t
* @return {string}
*/
var minWindow = function (s, t) {
let result = "";
let l = 0; // 初始左指针
let r = 0; // 初始右指针
const map = new Map(); // 创建字典表示子串所需的字符及其个数
for (let i = 0, len = t.length; i < len; i++) {
const c = t[i]; // 设置字典中所需字符的个数
map.set(c, map.has(c) ? map.get(c) + 1 : 1);
}
let mapType = map.size; // 记录还需要匹配的字符数
while (r < s.length) { // 逐个移动右指针
// 如果是需要匹配的字符,更新字典和还需要的字符数
const c = s[r];
if (map.has(c)) {
map.set(c, map.get(c) - 1);
if (map.get(c) === 0) mapType -= 1;
}
// 当需要匹配的字符已经集齐时,开始逐个移动左指针,尽可能减少子串长度
while (mapType === 0) {
// 当新的窗口字符长度小于之前的字符长度时,更新结果
const newRes = s.slice(l, r + 1);
if (!result || newRes.length < result.length) result = newRes;
// 如果是需要匹配的字符,更新字典和还需要的字符数
const c2 = s[l];
if (map.has(c2)) {
map.set(c2, map.get(c2) + 1);
if (map.get(c2) === 1) mapType += 1;
// 此时左指针不能再移动了,跳出循环去移动右指针,重新找到所需的字符串
}
l++;
}
r++;
}
return result;
};
【LC】347. 前 K 个高频元素
https://leetcode.cn/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/
- 题目
- 解法1
- 解法2
输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
输出: [1,2]
输入: nums = [1], k = 1
输出: [1]
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number[]}
*/
var topKFrequent = function (nums, k) {
// ...
};
输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
输出: [1,2]
输入: nums = [1], k = 1
输出: [1]
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number[]}
*/
var topKFrequent = function (nums, k) {
if (nums.length === 1) return nums
const obj = {}
nums.forEach(item => {
if (!obj[item]) {
obj[item] = 1
} else {
obj[item]++
}
})
const arr = []
for (let key in obj) {
arr.push({
key,
val: obj[key]
})
}
arr.sort((a, b) => b['val'] - a['val'])
const result = []
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result.push(arr[i].key)
}
return result
};
输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
输出: [1,2]
输入: nums = [1], k = 1
输出: [1]
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number[]}
*/
var topKFrequent = function (nums, k) {
if (nums.length === 1) return nums
const obj = {}
nums.forEach(item => {
if (!obj[item]) {
obj[item] = 1
} else {
obj[item]++
}
})
const arr = [...new Set(nums)]
arr.sort((a, b) => obj[b] - obj[a])
return arr.slice(0, k)
};
【LC】374. 猜数字大小
https://leetcode.cn/problems/guess-number-higher-or-lower/
- 题目
- 答案
输入:n = 10
输出:6
// 每轮游戏,我都会从 1 到 n 随机选择一个数字。 请你猜选出的是哪个数字。
// 如果你猜错了,我会告诉你,你猜测的数字比我选出的数字是大了还是小了。
// 提供一个 guess 方法,返回值如下:
// -1:我选出的数字比你猜的数字小 pick < num
// 1:我选出的数字比你猜的数字大 pick > num
// 0:我选出的数字和你猜的数字一样。恭喜!你猜对了!pick == num
/**
* Forward declaration of guess API.
* @param {number} num your guess
* @return -1 if num is higher than the picked number
* 1 if num is lower than the picked number
* otherwise return 0
* var guess = function(num) {}
*/
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var guessNumber = function (n) {
// ...
};
输入:n = 10
输出:6
// 每轮游戏,我都会从 1 到 n 随机选择一个数字。 请你猜选出的是哪个数字。
// 如果你猜错了,我会告诉你,你猜测的数字比我选出的数字是大了还是小了。
// 提供一个 guess 方法,返回值如下:
// -1:我选出的数字比你猜的数字小 pick < num
// 1:我选出的数字比你猜的数字大 pick > num
// 0:我选出的数字和你猜的数字一样。恭喜!你猜对了!pick == num
/**
* Forward declaration of guess API.
* @param {number} num your guess
* @return -1 if num is higher than the picked number
* 1 if num is lower than the picked number
* otherwise return 0
* var guess = function(num) {}
*/
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var guessNumber = function (n) {
let left = 1;
let right = n;
while (left < right) { // 循环直至区间左右端点相同
const mid = Math.floor(left + (right - left) / 2);
if (guess(mid) <= 0) {
right = mid; // 答案在区间 [left, mid] 中
} else {
left = mid + 1; // 答案在区间 [mid+1, right] 中
}
}
// 此时有 left == right,区间缩为一个点,即为答案
return left;
};
两两相加且不重复
给出一个数组,以及一个值。求数组中 两两相加的和等于该值的集合 有多少个?(如 8 + 1 与 1 + 8 重复,只记一次)
- 示例
- 答案
const arr = [1, 3, 8, 6, 1];
fn(arr, 9); // 返回2(符合条件:1+8、3+6)
fn(arr, 4); // 返回1(符合条件:1+3)
fn(arr, 5); // 返回0(无符合条件的组合)
function fn(arr, target) {
const validPairs = new Set(); // 存储符合条件的数对(字符串形式)
// 双重循环遍历所有可能的数对
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] + arr[j] === target) {
// 将数对排序并转为字符串(确保 [1,8] 和 [8,1] 被视为相同)
const pair = [arr[i], arr[j]].sort((a, b) => a - b);
validPairs.add(pair.join(','));
}
}
}
return validPairs.size; // 返回去重后的数对数量
}
// 示例用法
console.log(fn([1, 3, 8, 6, 1], 9)); // 输出 2(1+8、3+6)
console.log(fn([1, 3, 8, 6, 1], 4)); // 输出 1(1+3)
console.log(fn([1, 3, 8, 6, 1], 5)); // 输出 0
链表系列
【LC】237. 删除链表中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/
- 题目
- 答案
输入:head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5
输出:[4,1,9]
解释:指定删除节点 5,调用后链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} node
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify node in-place instead.
*/
var deleteNode = function (node) {
// ...
};
输入:head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5
输出:[4,1,9]
解释:指定删除节点 5,调用后链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} node
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify node in-place instead.
*/
var deleteNode = function (node) {
node.val = node.next.val
node.next = node.next.next
};
【LC】206. 反转链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
- 题目
- 答案
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
输入:head = []
输出:[]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseList = function (head) {
// ...
};
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
输入:head = []
输出:[]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseList = function (head) {
let p1 = head
let p2 = null
while (p1) {
const temp = p1.next
p1.next = p2
p2 = p1
p1 = temp
}
return p2
};
【LC】2. 两数相加
https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-two-numbers/
- 题目
- 答案
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出:[7,0,8]
解释:342 + 465 = 807
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var addTwoNumbers = function (l1, l2) {
// ...
};
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出:[7,0,8]
解释:342 + 465 = 807
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var addTwoNumbers = function (l1, l2) {
const l3 = new ListNode(0)
let p1 = l1
let p2 = l2
let p3 = l3
let carry = 0
while (p1 || p2) {
const val1 = p1 ? p1.val : 0
const val2 = p2 ? p2.val : 0
const sum = val1 + val2 + carry
carry = Math.floor(sum / 10)
p3.next = new ListNode(sum % 10)
if (p1) {
p1 = p1.next
}
if (p2) {
p2 = p2.next
}
p3 = p3.next
}
if (carry) {
p3.next = new ListNode(carry)
}
return l3.next
};
【LC】83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/
- 题目
- 答案
输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3]
输出:[1,2,3]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var deleteDuplicates = function (head) {
// ...
};
输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3]
输出:[1,2,3]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var deleteDuplicates = function (head) {
let p = head
while (p) {
if (p.val === p.next?.val) {
p.next = p.next.next
} else {
p = p.next
}
}
return head
};
【LC】141. 环形链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/
- 题目
- 答案
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasCycle = function (head) {
// ...
};
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasCycle = function (head) {
let p1 = head
let p2 = head
while (p1 && p2) {
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next?.next
if (p1 === p2) {
return true
}
}
return false
};
【LC】21. 合并两个有序链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
- 题目
- 答案
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} list1
* @param {ListNode} list2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function (list1, list2) {
// ...
};
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} list1
* @param {ListNode} list2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function (list1, list2) {
const head = new ListNode()
let p = head
while (list1 && list2) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
p.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
} else {
p.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
}
p = p.next
}
if (list1) p.next = list1
if (list2) p.next = list2
return head.next
};
【LC】23. 合并 K 个升序链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
- 题目
- 解法1
- 解法2
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode[]} lists
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeKLists = function (lists) {
// ...
};
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode[]} lists
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeKLists = function (lists) {
const len = lists.length
if (len === 0) return null
const merge = (l1, l2) => { // 两两合并
const head = new ListNode()
let p = head
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
p.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
} else {
p.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
}
p = p.next
}
p.next = l1 ? l1 : l2
return head.next
}
let result = lists[0]
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
if (lists[i]) {
result = merge(result, lists[i])
}
}
return result
};
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode[]} lists
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeKLists = function (lists) {
const arr = []
lists.forEach(item => {
let p = item
while (p) {
arr.push(p.val)
p = p.next
}
})
arr.sort((a, b) => a - b)
const result = new ListNode()
let p = result
arr.forEach(item => {
p.next = new ListNode(item)
p = p.next
})
return result.next
};
二叉树系列
DFS 和 BFS 的区别,手写 DFS 和 BFS(ing)
深度优先遍历是尽可能深的搜索树的分支,而广度优先遍历是先访问根节点最近的节点。
const dfs = root => {
console.log(root.val)
root.children.forEach(dfs)
}
dfs(tree)
const bfs = root => {
const queue = []
if (root) queue.push(root)
while (queue.length) {
const curNode = queue.shift()
console.log(curNode.val)
curNode.children.forEach(child => {
queue.push(child)
})
}
}
bfs(tree)
二叉树前 / 中 / 后 / 层序遍历结果

- 题目
- 答案
上面二叉树先/中/后/层序遍历的结果为?
前序遍历(中左右)
5 4 1 2 6 7 8
中序遍历(左中右)
1 4 2 5 7 6 8
后序遍历(左右中)
1 2 4 7 8 6 5
层序遍历(广度优先遍历)
[[5],[4,6],[1,2,7,8]]
【LC】144. 二叉树的前序遍历(两种解法)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/
- 题目
- 递归解法
- 非递归解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
const preorderTraversal = (root) => {
// ...
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
const preorderTraversal = (root) => {
let result = []
const preorder = (node) => {
if (!node) return
// 先根节点
result.push(node.val)
// 然后遍历左子树
preorder(node.left)
// 再遍历右子树
preorder(node.right)
}
preorder(root)
return result
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
// 前序遍历
const preorderTraversal = (root) => {
const result = [];
const stack = [];
// 当根节点不为空的时候,将根节点入栈
if (root) stack.push(root)
while (stack.length) {
const curNode = stack.pop()
// 第一步的时候,先访问的是根节点
result.push(curNode.val)
// 我们先打印左子树,然后右子树
// 所以先加入栈的是右子树,然后左子树
curNode.right && stack.push(curNode.right)
curNode.left && stack.push(curNode.left)
}
return result
}
【LC】94. 二叉树的中序遍历(两种解法)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
- 题目
- 递归解法
- 非递归解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
const inorderTraversal = function (root) {
// ...
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
const inorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = []
const inorder = node => {
if (!node) return
inorder(node.left)
result.push(node.val)
inorder(node.right)
}
inorder(root)
return result
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
const inorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = [];
const stack = [];
while (root) { // 能压栈的左子节点都压进来
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
while (stack.length) {
let curNode = stack.pop(); // 栈顶的节点出栈
result.push(curNode.val); // 在压入右子树之前,处理它的数值部分(因为中序遍历)
curNode = curNode.right; // 获取它的右子树
while (curNode) { // 右子树存在,执行 while 循环
stack.push(curNode); // 压入当前 root
curNode = curNode.left; // 不断压入左子节点
}
}
return result;
};
【LC】145. 二叉树的后序遍历(两种解法)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
- 题目
- 递归解法
- 非递归解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
const postorderTraversal = function (root) {
// ...
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
const postorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = []
const postorder = node => {
if (!node) return
postorder(node.left)
postorder(node.right)
result.push(node.val)
}
postorder(root)
return result
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
const postorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = [];
const stack = [];
// 当根节点不为空的时候,将根节点入栈
if (root) stack.push(root)
while (stack.length) {
const curNode = stack.pop()
// 中左右 => 右左中
result.unshift(curNode.val)
// 先进栈左子树后右子树
// 出栈的顺序就变更为先右后左
curNode.left && stack.push(curNode.left)
curNode.right && stack.push(curNode.right)
}
return result
}
【LC】102. 二叉树的层序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
- 题目
- 答案
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输入:root = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
输出:[[3], [9, 20], [15, 7]]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
const levelOrder = function (root) {
// ...
};
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输入:root = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
输出:[[3], [9, 20], [15, 7]]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
const levelOrder = function (root) {
const result = [];
const queue = [];
if (root) queue.push(root);
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length; // 记录当前层级节点数
const curArr = []; // 存放每一层的节点
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const curNode = queue.shift();
curArr.push(curNode.val);
// 存放当前层下一层的节点
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left);
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right);
}
result.push(curArr); // 把每一层的结果放到结果数组
}
return result;
};
【LC】104. 二叉树的最大深度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
- 题目
- DFS 解法
- BFS 解法
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输入:root = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
输出:3
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function (root) {
// ...
};
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输入:root = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
输出:3
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function (root) {
if (!root) return 0
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1
};
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输入:root = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
输出:3
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function (root) {
let result = 0;
const queue = [];
if (root) queue.push(root);
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const curNode = queue.shift();
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left);
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right);
}
result += 1;
}
return result;
};
【LC】111. 二叉树的最小深度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点(没有子节点的节点)的最短路径上的节点数。
- 题目
- DFS 解法
- BFS 解法
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输入:root = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
输出:2
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var minDepth = function (root) {
// ...
};
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输入:root = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
输出:2
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var minDepth = function (root) {
if (!root) return 0;
if (root.left && root.right) {
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
if (root.left) {
return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
}
if (root.right) {
return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
}
return 1;
};
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输入:root = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
输出:2
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var minDepth = function (root) {
let result = 0;
const queue = [];
if (root) queue.push(root);
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const curNode = queue.shift();
if (!curNode.left && !curNode.right) {
return result + 1; // 如果是叶子节点,直接返回所在层数
}
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left);
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right);
}
result += 1; // 进入下一层
}
return result
};
【LC】112. 路径总和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/
- 题目
- 答案
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} targetSum
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasPathSum = function (root, targetSum) {
// ...
};
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} targetSum
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasPathSum = function (root, targetSum) {
if (!root) return false
let result = false
const dfs = (node, sum) => {
if (!node.left && !node.right && sum === targetSum) {
result = true
}
node.left && dfs(node.left, sum + node.left.val)
node.right && dfs(node.right, sum + node.right.val)
}
dfs(root, root.val)
return result
};
计算二叉树的深度
某公司组织架构以二叉树形式记录,请返回该公司的层级数(即二叉树的最大深度,定义为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数)。
1
2 2
3 5
4 4
输出示例:
- 输入:
root = [1,2,2,3,null,null,5,4,null,null,4](二叉树的数组表示,遵循层序遍历规则,null代表空节点) - 输出:
4 - 解释:最长路径为
1→2→3→4或1→2→5→4,路径包含 4 个节点,因此层级数为 4。
解法:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function(root) {
// 空节点的深度为 0
if (root === null) {
return 0;
}
// 递归计算左子树的深度
const leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
// 递归计算右子树的深度
const rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
// 当前节点的深度 = 左右子树深度的最大值 + 1(自身)
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
};